Je vais vous expliquer comment établir une connexion entre un serveur Windows et Ansible, ce dernier étant exécuté sur une machine Ubuntu.
Pour reproduire les étapes décrites ci-dessous, assurez-vous que Python 3.x et Ansible sont installés sur les deux systèmes. Si vous avez besoin d’aide, vous pouvez consulter les articles suivants :
Comment installer et configurer Ansible sur Ubuntu ?
Comment installer Ansible sur Windows ?
Voici les informations des deux serveurs que j’utiliserai pour cette démonstration :
- Contrôleur Ansible : 192.168.0.108
- Serveur Windows : 192.168.0.102
Étape 1 : Création d’un utilisateur Windows pour Ansible
Commencez par créer un nouvel utilisateur dédié à la connexion Ansible sur votre serveur Windows.
- Ouvrez l’outil « Gestion de l’ordinateur » sur votre système Windows, puis naviguez vers « Utilisateurs et groupes locaux ».
- Cliquez avec le bouton droit sur « Utilisateurs » et sélectionnez « Nouvel utilisateur ».
- Cochez la case « Le mot de passe n’expire jamais » et validez la création.
- Dans la liste des groupes, faites un clic droit sur « Administrateurs » puis « Propriétés ».
- Cliquez sur « Ajouter » et entrez « ansible » comme nom d’objet.
- Validez en cliquant sur « Vérifier les noms » puis « OK ».
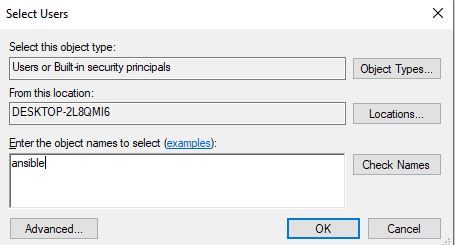
L’utilisateur « ansible » est maintenant configuré sur votre machine Windows.
Étape 2 : Installation des bibliothèques et configuration de WinRM
Sur votre machine contrôleur Ansible, mettez à jour votre système puis installez les bibliothèques nécessaires :
[email protected]:~$ sudo apt-get update [email protected]:~$ sudo apt-get install gcc python-dev [email protected]:~$ sudo apt install python3-pip
WinRM (Windows Remote Management) est un service qui permet de gérer à distance des systèmes Windows. Nous allons installer python3-winrm, un client Python utilisé pour établir la connexion avec le système Windows.
[email protected]:~$ sudo apt-get install python3-winrm Reading package lists... Done Building dependency tree Reading state information... Done The following packages were automatically installed and are no longer required: gyp libc-ares2 libhttp-parser2.8 libjs-async libjs-inherits libjs-is-typedarray libjs-node-uuid libuv1 libuv1-dev node-abbrev node-ajv node-ansi node-ansi-color-table node-ansi-regex node-ansi-styles node-ansistyles node-aproba node-archy node-are-we-there-yet node-async node-validate-npm-package-license node-wcwidth.js node-which node-which-module node-wide-align node-wrap-ansi node-wrappy node-y18n node-yallist node-yargs node-yargs-parser nodejs nodejs-doc Use 'sudo apt autoremove' to remove them. The following additional packages will be installed: python3-kerberos python3-ntlm-auth python3-requests-kerberos python3-requests-ntlm python3-xmltodict The following NEW packages will be installed: python3-kerberos python3-ntlm-auth python3-requests-kerberos python3-requests-ntlm python3-winrm python3-xmltodict 0 upgraded, 6 newly installed, 0 to remove and 231 not upgraded. Need to get 84.8 kB of archives. After this operation, 442 kB of additional disk space will be used. Do you want to continue? [Y/n] Y Get:1 http://old-releases.ubuntu.com/ubuntu cosmic/universe amd64 python3-kerberos amd64 1.1.14-1build1 [16.8 kB] Get:2 http://old-releases.ubuntu.com/ubuntu cosmic/universe amd64 python3-ntlm-auth all 1.1.0-1 [19.6 kB] Get:3 http://old-releases.ubuntu.com/ubuntu cosmic/universe amd64 python3-requests-kerberos all 0.11.0-2 [10.1 kB] Get:4 http://old-releases.ubuntu.com/ubuntu cosmic/universe amd64 python3-requests-ntlm all 1.1.0-1 [6,004 B] Get:5 http://old-releases.ubuntu.com/ubuntu cosmic/universe amd64 python3-xmltodict all 0.11.0-2 [10.6 kB] Get:6 http://old-releases.ubuntu.com/ubuntu cosmic/universe amd64 python3-winrm all 0.3.0-2 [21.7 kB] Fetched 84.8 kB in 1s (70.3 kB/s) Selecting previously unselected package python3-kerberos. (Reading database ... 244430 files and directories currently installed.) Preparing to unpack .../0-python3-kerberos_1.1.14-1build1_amd64.deb ... Unpacking python3-kerberos (1.1.14-1build1) ... Selecting previously unselected package python3-ntlm-auth. Selecting previously unselected package python3-xmltodict. Preparing to unpack .../4-python3-xmltodict_0.11.0-2_all.deb ... Unpacking python3-xmltodict (0.11.0-2) ... Selecting previously unselected package python3-winrm. Preparing to unpack .../5-python3-winrm_0.3.0-2_all.deb ... Unpacking python3-winrm (0.3.0-2) ... Setting up python3-kerberos (1.1.14-1build1) ... Setting up python3-winrm (0.3.0-2) ...
Étape 3 : Mise à jour du fichier d’inventaire Ansible
Modifiez maintenant le fichier d’inventaire Ansible en ajoutant l’adresse IP de votre serveur Windows. Ansible pourra ainsi identifier la machine à laquelle se connecter.
[email protected]:~$ sudo gedit /etc/ansible/hosts [win] 192.168.0.102
Étape 4 : Configuration des variables de groupe Ansible
Créez un répertoire pour stocker les variables nécessaires à la connexion au serveur Windows.
[email protected]:~$ mkdir /etc/ansible/group_vars [email protected]:~$ sudo chmod -R 777 /etc/ansible/
Créez un fichier `win.yaml` et renseignez-y les informations de l’utilisateur créé lors de la première étape, ainsi que d’autres variables nécessaires à la connexion au système Windows.
[email protected]:~$ gedit /etc/ansible/group_vars/win.yaml
--- ansible_user: ansible ansible_password: ansible ansible_connection: winrm ansible_winrm_server_cert_validation: ignore ansible_winrm_transport: basic ansible_winrm_port: 5985 ansible_python_interpreter: C:Userstoptips.frAppDataLocalProgramsPythonPython37python
Étape 5 : Configuration du serveur Windows pour la gestion
Ouvrez PowerShell sur votre serveur Windows et assurez-vous qu’il est à jour. Powershell 3.0 et .NET Framework 4.0 doivent être installés.
PS C:WINDOWSsystem32> $url = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/jborean93/ansible-windows/master/scripts/Upgrade-PowerShell.ps1" PS C:WINDOWSsystem32> $file = "$env:tempUpgrade-PowerShell.ps1" PS C:WINDOWSsystem32> $username = "ansible" PS C:WINDOWSsystem32> $password = "ansible" PS C:WINDOWSsystem32> (New-Object -TypeName System.Net.WebClient).DownloadFile($url, $file) PS C:WINDOWSsystem32> Set-ExecutionPolicy -ExecutionPolicy Unrestricted -Force PS C:WINDOWSsystem32> &$file -Version 5.1 -Username $username -Password $password -Verbose
Pour configurer WinRM avec Ansible, utilisez le script de configuration fourni. Exécutez ce script dans PowerShell.
PS C:WINDOWSsystem32> $url = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ansible/ansible/devel/examples/scripts/ConfigureRemotingForAnsible.ps1" PS C:WINDOWSsystem32> $file = "$env:tempConfigureRemotingForAnsible.ps1" PS C:WINDOWSsystem32> (New-Object -TypeName System.Net.WebClient).DownloadFile($url, $file) PS C:WINDOWSsystem32> powershell.exe -ExecutionPolicy ByPass -File $file PS C:WINDOWSsystem32> winrm enumerate winrm/config/Listener Listener Address = * Transport = HTTP Port = 5985 Hostname Enabled = true URLPrefix = wsman CertificateThumbprint ListeningOn = 127.0.0.1, 169.254.8.240, 169.254.36.9, 169.254.102.217, 169.254.215.170, 192.168.0.102, ::1, fe80::3131:c6d7:9ef5:8f0%7, fe80::51b7:9134:550d:d7aa%22, fe80::88f1:1229:e1dd:2409%16, fe80::99cf:5796:4f8e:f5c1%15, fe80::fd77:c19d:e0f2:66d9%9 Listener Address = * Transport = HTTPS Port = 5986 Hostname = DESKTOP-2L8QMI6 Enabled = true URLPrefix = wsman CertificateThumbprint = C83B3FC8B274D0B650F0FD647DC7AC129BBE3FA0 ListeningOn = 127.0.0.1, 169.254.8.240, 169.254.36.9, 169.254.102.217, 169.254.215.170, 192.168.0.102, ::1, fe80::3131:c6d7:9ef5:8f0%7, fe80::51b7:9134:550d:d7aa%22, fe80::88f1:1229:e1dd:2409%16, fe80::99cf:5796:4f8e:f5c1%15, fe80::fd77:c19d:e0f2:66d9%9
Configurez WinRM pour autoriser le trafic HTTP.
PS C:WINDOWSsystem32> winrm set winrm/config/service '@{AllowUnencrypted="true"}'
Service
RootSDDL = O:NSG:BAD:P(A;;GA;;;BA)(A;;GR;;;IU)S:P(AU;FA;GA;;;WD)(AU;SA;GXGW;;;WD)
MaxConcurrentOperations = 4294967295
MaxConcurrentOperationsPerUser = 1500
EnumerationTimeoutms = 240000
MaxConnections = 300
MaxPacketRetrievalTimeSeconds = 120
AllowUnencrypted = true
Auth
Basic = true
Kerberos = true
Negotiate = true
Certificate = false
CredSSP = false
CbtHardeningLevel = Relaxed
DefaultPorts
HTTP = 5985
HTTPS = 5986
IPv4Filter = *
IPv6Filter = *
EnableCompatibilityHttpListener = false
EnableCompatibilityHttpsListener = false
CertificateThumbprint
AllowRemoteAccess = true
Activez l’authentification basique dans WinRM.
PS C:WINDOWSsystem32> winrm set winrm/config/service/auth '@{Basic="true"}'
Auth
Basic = true
Kerberos = true
Negotiate = true
Certificate = false
CredSSP = false
CbtHardeningLevel = Relaxed
Étape 6 : Test de la connexion au serveur Windows
Toutes les étapes de configuration sont maintenant terminées. Retournez sur votre contrôleur Ansible et utilisez le module `win_ping` pour tester la connexion avec votre serveur Windows.
[email protected]:~$ ansible win -m win_ping
192.168.0.102 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
Un message de succès indique que la connexion est établie. Votre serveur Windows est maintenant prêt à être géré à distance depuis Ansible sur Ubuntu.